

Craif has developed a simple and effective method for exosome
enrichment using nano-fabrication technology
Within our bodies, a myriad of intercellular communications transpire beyond a single-cell level, facilitated by the transfer of exosomes released by cells to other cells. In particular, exosomes released by cancer cells have been shown to contain molecules related to angiogenesis, metastasis, and immune evasion, playing a crucial role in creating a microenvironment conducive to cancer progression. At Craif, we utilize the NANO IP™ (NANO Intelligence Platform) to interpret the crosstalk between cells concerning cancer and many other diseases.
At the heart of Craif’s technology lies our expertise in nano-material development. By utilizing tools like microfluidic nanowire devices®️ and cellulose nanofibers, among others, we efficiently capture biomarkers. This enables sensitive detection of trace biomarkers such as microRNA, aiding in the identification of useful biomarkers.

The identification of useful biomarkers is pivotal; for their practical diagnostic application, enhanced quantification and reproducibility are key. At Craif, we develop cutting-edge analytical and measurement systems to improve the quantification and reproducibility of challenging microRNA and other trace nucleic acid analyses.

Measurement data accrued daily is stored alongside clinical information, accumulating a dataset unparalleled in scale. Our dedicated team of data scientists leverages state-of-the-art artificial intelligence and advanced statistical analysis to develop algorithms capable of accurately estimating the risks of various diseases.

Within the Craif lab, the processes from specimen management to measurement and digitization are highly automated, enables stable and high-throughput measurements. Thorough R&D and the digital transformation (DX) of the measurement workflow mitigate human errors, realizing operations of high productivity and transparency.
All experimental data executed in the digital CLL are aggregated in the database along with the linked clinical information on the specimens. Instant cross-analysis and retrospection of patient backgrounds and experimental conditions enable verification of biomarker behavior from various angles, alongside seamless analysis utilizing big data.
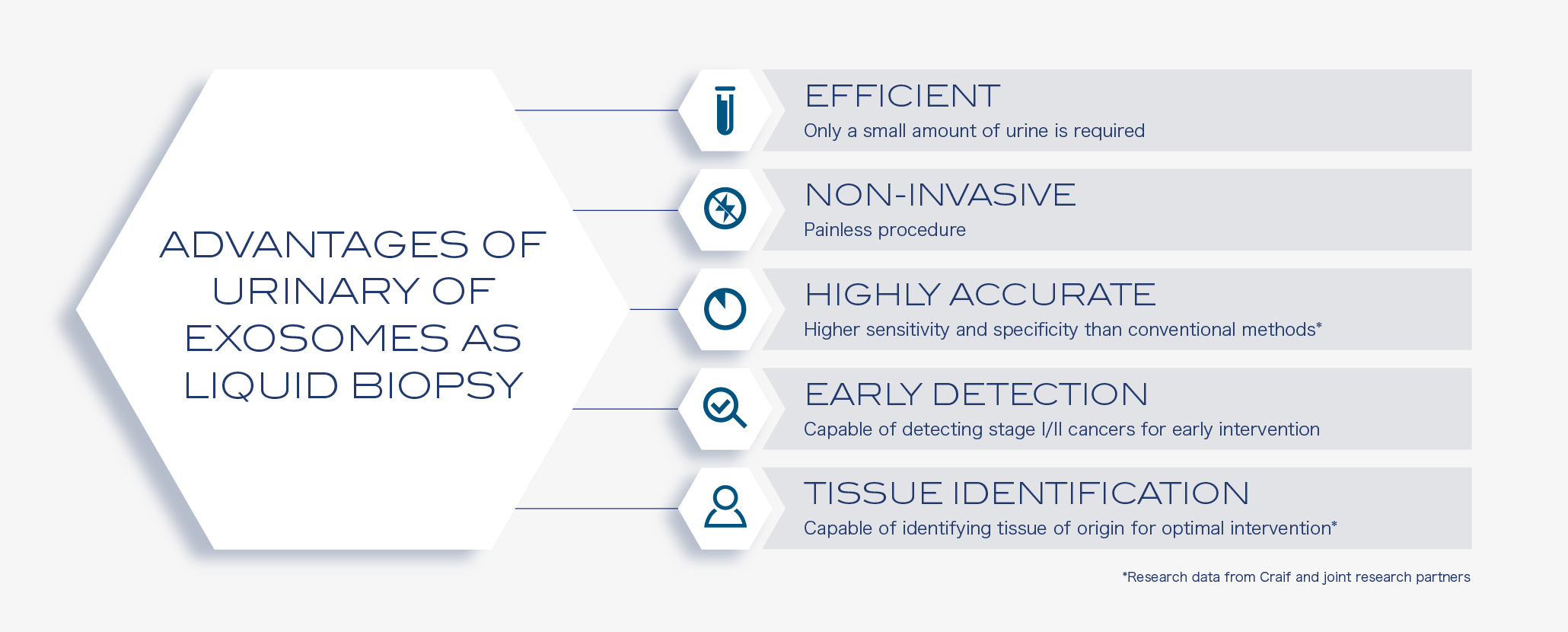
Cancer cells need to communicate with other cells to survive by secreting exosomes that contain various proteins, mRNAs, and miRNAs. Communications between cancer and its microenvironment, including stromal and distant cells, can promote tumor growth, metastasis, and escape from immune surveillance. By capturing exosomes comprehensively, we can understand not only the characteristics of the cancer cells, but also its microenvironment reflecting the host response to the disease. To put it simply, we can catch a glimpse of the cancer-host conversations from the extracted exosomes. It is through this means that we can detect cancer even in a very early stage, in which cancer tissue is not large enough to be detected by other approaches such as CTC and cfDNA analysis. By measuring urinal microRNA from exosome extracted by this device and analyzing the samples using machine learning algorithms, we sucessfully developed an algorithm to distinguish cancer from non-cancer samples with high sensitivity and specificity in seven cancer types.
Urinary MicroRNAs as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Biomarkers and its potential for accurate assessment of disease severity
ACR Convergence 2021
Urinary MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer
The 80th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Cancer Association
リキッドバイオプシーにおける尿中microRNAの可能性
第41回日本分子腫瘍マーカー研究会